46+ Second Order Integrated Rate Law Equation
Second Order Integrated Rate Law Equation. 2a products or a + b products (when [a] = [b]) , rate = k[a] 2 the integrated rate law is 1/[a] = kt + 1/[a o ] 𝑅 p =− [𝑨] 𝒕 = [𝑨] we separate the variables and integrate over the interval:

When the integrated rate law is written in this way, a plot of ln[a] versus t will yield a. A chemist calls them second orderrate lawsbecause the rate is. If the plot is not a straight line, then.
solivette 5m brico depot siphon horizontal leroy merlin salle de bains meuble noir siege auto bebe confort milofix
PPT The Ultimate BOD PowerPoint Presentation, free
Considering the scenario where one second order reactant forms a given product in a chemical reaction, the differential rate law equation can be written as follows: Considering the scenario where one second order reactant forms a given product in a chemical reaction, the differential rate law equation can be written as follows: Differential and integrated rate equation for second order reactions. ∫ [ ] [ ]2 [𝐴] [𝐴]0 =− g∫ 𝑡 𝑡0 recall from calculus that (or check a table of integrals):

Additionally, what is the integrated rate law for a first order reaction? −d[r] dt = k[r]2 − d [ r] d t = k [ r] 2. The equation for the second order integrated rate law takes the form y = mx +b, where y = 1/a; The integral form of the equation was obtained from the differential form and.

This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into chemical kinetics. Thus, the graph of the second order integrated rate law is a straight. = k2t + 1 [a]o. Considering the scenario where one second order reactant forms a given product in a chemical reaction, the differential rate law equation can be written as follows: If the plot is not.

𝑅 p =− [𝑨] 𝒕 = [𝑨] we separate the variables and integrate over the interval: A chemist calls them second orderrate lawsbecause the rate is. Here are a number of highest rated integrated rate law second order equation pictures on internet. This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into chemical kinetics. Integrated rate law second order equation.

(k = slope of line) examples. ∫ [ ] [ ]2 [𝐴] [𝐴]0 =− g∫ 𝑡 𝑡0 recall from calculus that (or check a table of integrals): Its submitted by organization in the best field. Considering the scenario where one second order reactant forms a given product in a chemical reaction, the differential rate law equation can be written as.
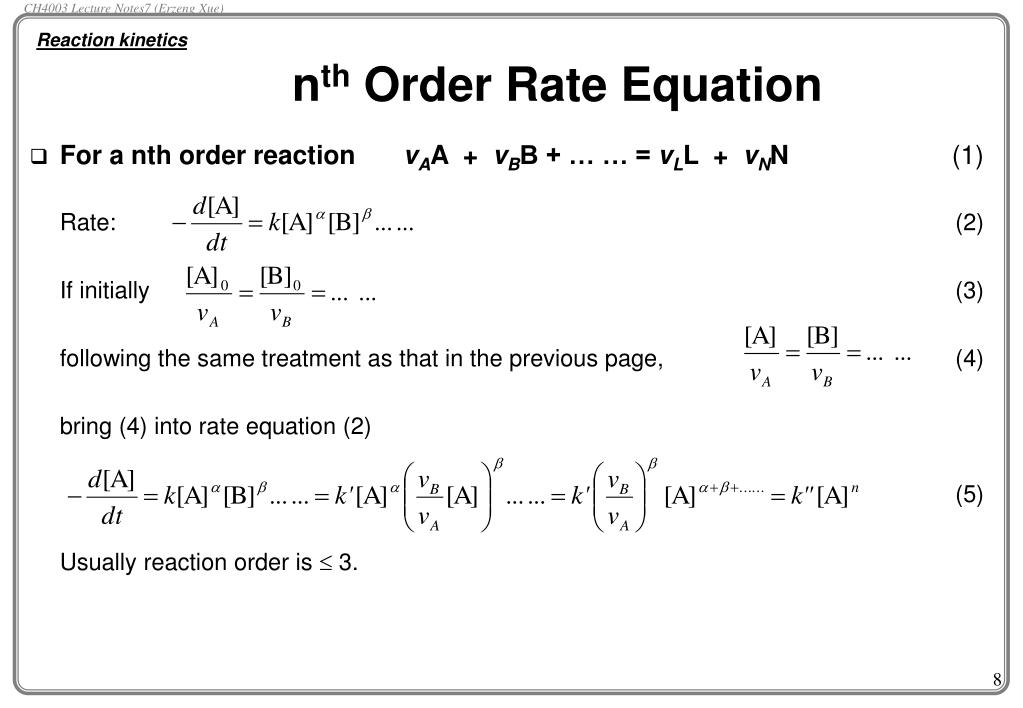
𝑅 p =− [𝑨] 𝒕 = [𝑨] we separate the variables and integrate over the interval: Thus, the graph of the second order integrated rate law is a straight. Because this equation has the form y = mx + b, a plot of the inverse of [a] as a function of time yields a straight line. Its submitted by organization.

Additionally, what is the integrated rate law for a first order reaction? 1 [a] = kt+ 1 [a]0 y = mx+b 1 [ a] = k t + 1 [ a] 0 y = m x + b. This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into chemical kinetics. If the plot is not a straight line, then. Considering the.

Considering the scenario where one second order reactant forms a given product in a chemical reaction, the differential rate law equation can be written as follows: Second order reactions ( j=2) the differential form of the rate law is: 2a products or a + b products (when [a] = [b]) , rate = k[a] 2 the integrated rate law is.